As OMRON’s corporate R&D unit, the Technology and Intellectual Property HQ is promoting initiatives to evolve OMRON’s core technologies, “Sensing & Control + Think,” to link these technologies to the creation of innovation driven by social needs that help solve social issues. In fiscal 2024, OMRON worked to achieve the goal of addressing the three social issues set under SF2030: “achievement of carbon neutrality,” “realization of a digital society,” and “extension of healthy life expectancy,” by strengthening collaboration with its businesses and promoting R&D initiatives. In particular, OMRON pursued technology development to drive growth in the Industrial Automation Business, including improving the accuracy of distance measurement sensors, enhancing usability in visual inspection, and supporting operational management of autonomous mobile robots (AMRs). In the Social Systems, Solutions and Service Business, we focused on developing more compact power conditioners. In the Healthcare Business, we advanced technology development to improve the accuracy of blood pressure monitors and electrocardiographs, further enhancing the strengths of our products.
Under Structural Reform Program NEXT 2025, amid the difficult reality of deteriorating business performance due to factors such as a slowdown in the Chinese economy, it has become clear that it is necessary to further evolve and accelerate technology management based on backcasting and forecasting, which OMRON has established over the years. Accordingly, led by the Technology and Intellectual Property HQ, we have launched initiatives to strengthen the linkage between our technology strategies and business strategies. What became clear through this process is that the essential management issues in realizing innovation driven by social needs, OMRON’s fundamental purpose, include returning to a customer-driven approach and improving development productivity.
To address these management issues, we launched companywide “technology governance initiatives” aimed at improving development productivity by reforming every phase of R&D, from technology exploration to product development, starting from the stage of setting challenges in OMRON Group’s technology management. In these initiatives, we are also working to redefine our focus areas of core technologies that the OMRON Group should pursue over the medium to long term in order to further enhance our innovation driven by social needs. As a result of these initiatives, we have already begun to implement specific measures such as strategic R&D investments, strengthening human resources, and making upfront investments in advanced technologies. Through these technology governance initiatives, we are steadily making progress, using the growth planning approach based on backcasting and forecasting, closely linked with our business strategies, to thoroughly enhance the competitiveness of our products (hardware) and to strengthen the business that combines products and services by leveraging this strength to convert on-site data into solutions and provide those solutions.
In this section, we describe the content and progress of the technology governance initiatives that aim to achieve sustainable growth by reinforcing our core technologies.
Through the review of the business management structure and structural reforms under NEXT 2025, we identified the following three key issues related to the OMRON Group’s technology management (see Table 1).
Decline in business competitiveness due to fragmented R&D investments
As R&D investments have been distributed across many businesses, the competitiveness of the businesses that support sales and profit has weakened.
Insufficient forward-looking investments to drive future growth
Approximately 70% of current R&D investments are concentrated on product development for existing businesses, resulting in a lack of forward-looking investments to support future growth.
Insufficient strategic reinforcement of R&D human resources
The Company has not yet established a sufficient framework to continuously enhance key companywide technology domains in coordination with its businesses, and consequently, the acquisition and development of R&D human resources have not been conducted strategically.
To address these issues, we worked to further advance our technology management, which has been established as OMRON’s business creation process (see Figure 1).
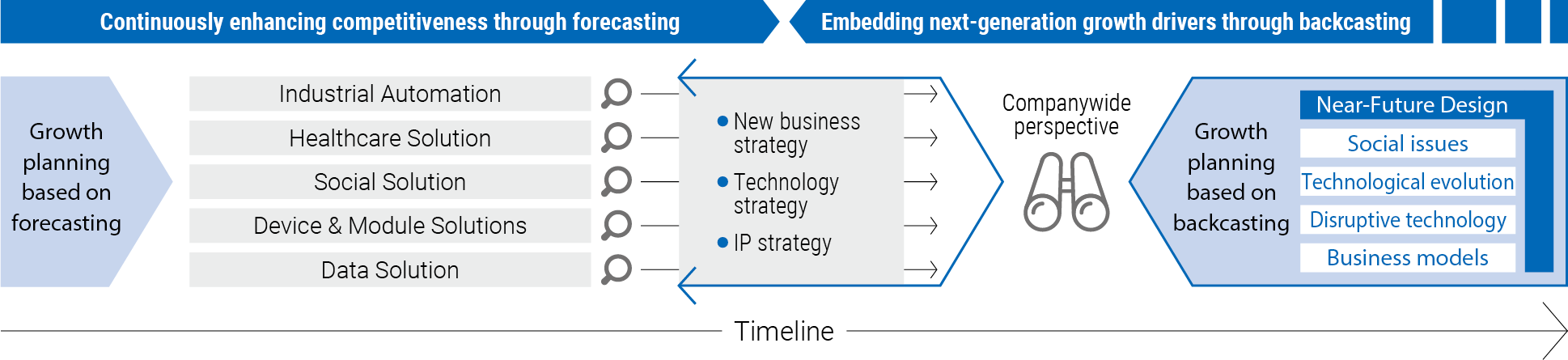
We are promoting initiatives to realize continuous enhancement of competitiveness based on forecasting, as well as to evolve our technology management based on backcasting to establish the drivers of next-generation growth and to continuously create innovation driven by social needs. Its realization requires strong decision-making and agile responses to change, and also calls for a companywide framework for making R&D investment decisions and the evolution of R&D activities across the OMRON Group. Accordingly, we launched group-wide technology governance initiatives to reform R&D from technology exploration to product development and to improve customer value generated through R&D investments, such as time and cost required for business creation (see Figure 2). These initiatives, closely linked with our businesses, are intended to identify technologies that leverage the business characteristics of the OMRON Group as a conglomerate that operates across multiple business domains, and to win in highly competitive markets through technological differentiation.
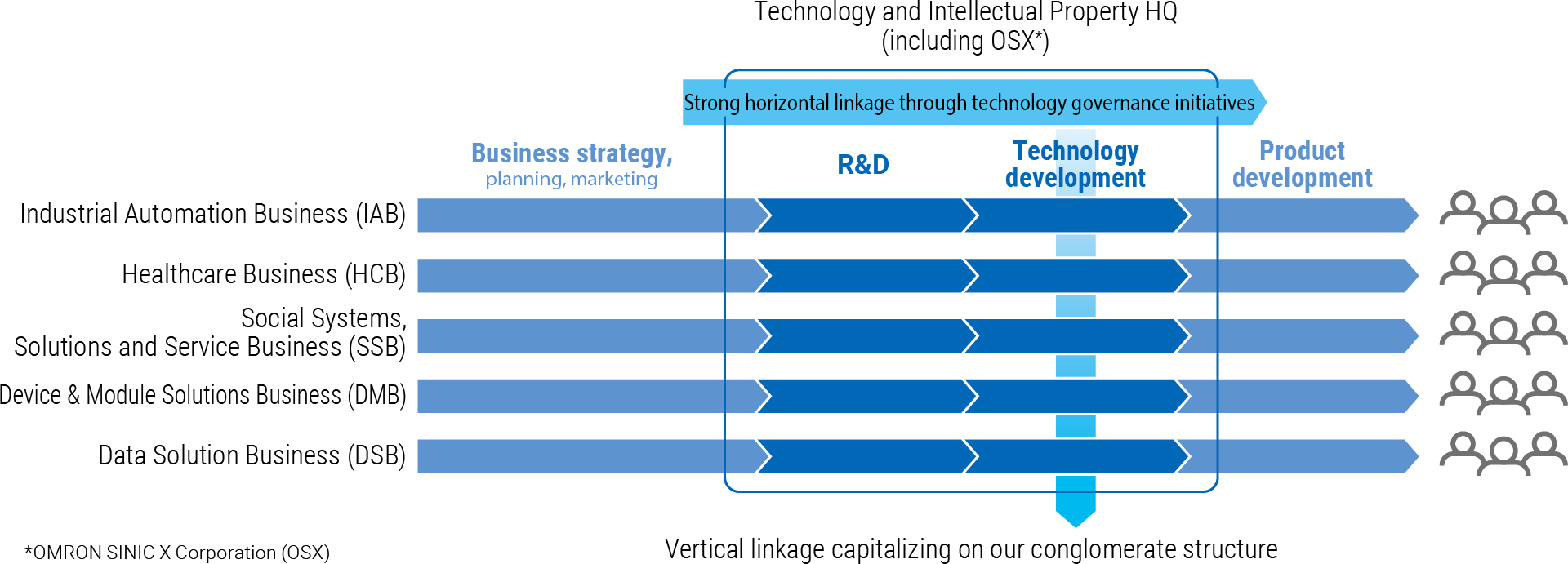
* Technology and Intellectual Property HQ (including OSX*)
In the technology governance initiatives, the OMRON Group reforms R&D from technology exploration to product development to improve the customer value generated through R&D investments, such as time and cost required for business creation, setting an indicator representing the OMRON Group’s competitiveness. We have positioned enhancing development productivity to a level that enables us to outperform competitors as a key factor for success (KFS) and are formulating key performance indicators (KPIs) to achieve this goal (see Figure 3).
KFS
Management decisions
Quality of strategy
Quality of execution
Operating level and rate
Quality of human resources
In particular, to enhance R&D productivity, we have launched reforms in each phase of R&D (technology development stages). This initiative aims to strengthen collaboration among management, business units, and the Technology and Intellectual Property HQ, and to promote efficient R&D in each phase based on a customer-value-oriented perspective.
Specifically, R&D based on both forecasting and backcasting will be promoted not separately by the business units and the Technology and Intellectual Property HQ, but collaboratively under a shared management policy. Accordingly, we restructured R&D as a consistent R&D pipeline from the phase of exploring scientific and academic value by setting future visions that reflect management’s aspirations to the phase of developing products and services that deliver customer value.
This consistent R&D pipeline enables us to build processes for each phase of R&D that link both forecasting and backcasting approaches, respond quickly to market changes, and enhance competitiveness. Through these technology governance initiatives launched in fiscal 2024, the Technology and Intellectual Property HQ, taking the lead and collaborating with the business units, is accelerating the development of a foundation for R&D aimed at thoroughly enhancing the competitiveness of our products (hardware) and leveraging this strength to transform on-site data into solutions that contribute to creating a business that combines products and services.
In fiscal 2025, we are focusing on strengthening the linkage between strategic R&D activities and businesses, as well as implementing multiple initiatives to define the next priority areas for future investment. Specifically, based on our medium- to long-term business strategies, the business units and the Technology and Intellectual Property HQ are working together to identify the technologies that will be required in the future and are incorporating them into respective technology strategies to accelerate technology development and business implementation. We are also examining the acquisition of new technologies that are difficult to explore through the extension of existing businesses from the perspective of backcasting, and updating the framework of the OMRON Group’s core technologies.
For updating the technology strategies, we are also utilizing quantitative analysis of intellectual property (IP) and intangible assets. As a result of creating many technologies, products, and services that help address social issues, OMRON has accumulated a wealth of unique intellectual property and intangible assets. Through a comprehensive analysis of OMRON’s intellectual property and intangible assets, it has become clear that among the approximately 60 business units across the Company, technology domains such as power electronics and optical sensing account for 5% to 10% of the total and are concentrated, and that these have been accumulated across multiple business units (see Figure 4).
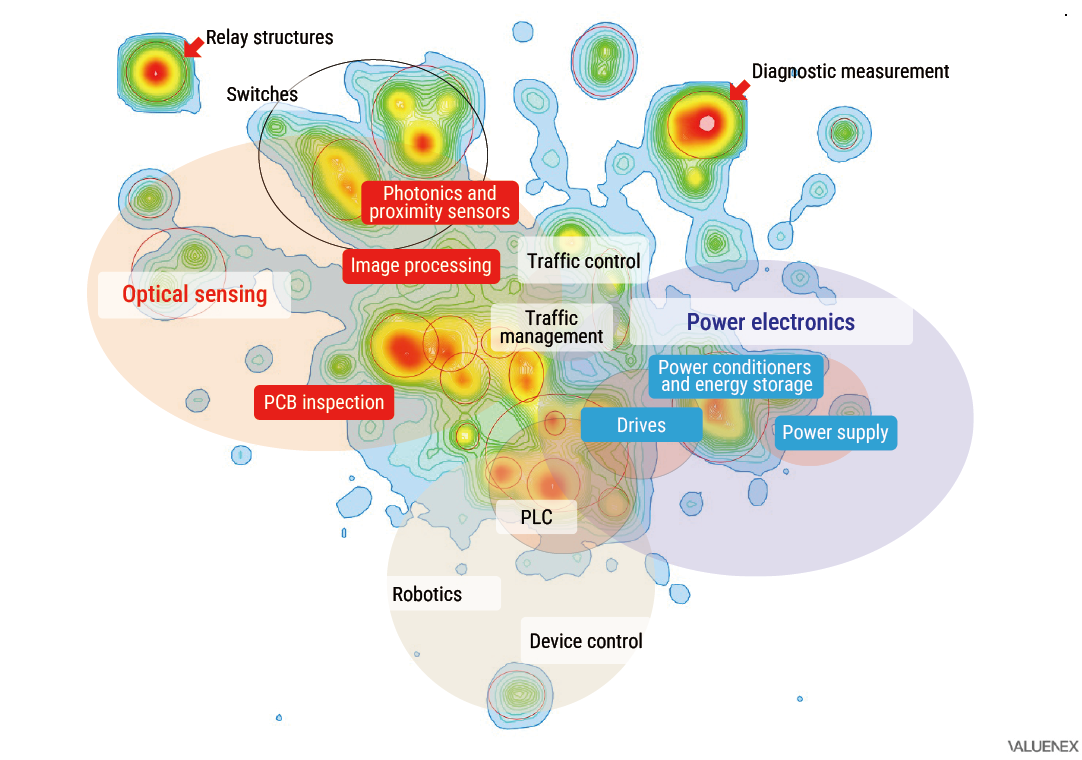
* Created by the Company using VALUENEX Radar, a comprehensive analysis tool provided by VALUENEX
Based on these findings, we are advancing updates to the technology strategies in the core technology “Sensing & Control + Think” to create value based on both forecasting and backcasting. We will define and strategically strengthen groups of technologies that drive business growth by evolving technologies to achieve manufacturing excellence based on forecasting from existing businesses, as well as by advancing technologies such as large-scale AI and data utilization and conducting frontier research that drives disruptive innovation in products based on backcasting.
Under technology strategies based on both forecasting and backcasting, we are accelerating OMRON’s sustainable value creation by promoting both short-term competitiveness enhancement and the establishment of a foundation for medium- to long-term growth through quantitative analysis of intellectual property and intangible assets.
Based on this concept, we began implementing initiatives to strengthen the power electronics domain, which involves the conversion and control of electric power. OMRON is advancing the development of power conditioners for solar power generation and energy storage systems integrated with EVs, as it has positioned “achievement of carbon neutrality” as one of the social issues to be addressed under SF2030. OMRON has accumulated intellectual property and other intangible assets over many years in technologies in the power electronics domain that support the higher efficiency and miniaturization of these devices. This power electronics domain is not limited to power conditioners and energy storage systems but also involves general-purpose power supplies and servo drives in the factory automation (FA) field. It is a technological domain where OMRON leverages its technological strengths across multiple businesses that it operates. In related markets within the power electronics domain, growth is expected in areas such as energy management, smart factories, and electric mobility. In particular, the market for energy storage systems is showing an annual growth rate of approximately 10%. Furthermore, reflecting the tightening of environmental regulations and growing environmental awareness, demand for high-efficiency power conversion technologies is expected to expand even further in the coming years.
At OMRON, we aim to achieve business growth exceeding the market growth rate in our existing businesses in the power electronics domain, including solar power generation systems, power control systems, industrial power supplies, and industrial servo drives.
Based on this idea, in order to execute our strategy as early as possible, OMRON officially announced its commitment to strengthening initiatives in the power electronics domain in a release dated May 12, 2025.
To maintain our competitive superiority, we need to demonstrate our strengths through more compact and higher-efficiency products. To this end, the development of multiple advanced technologies is essential, including the use of next-generation semiconductors for downsizing and higher efficiency, high-speed switching circuits, and thermal design technologies. In addition, in the field of energy management, it is necessary, in conjunction with data analysis using IoT and AI technologies, to evolve both circuit design technologies that expand compatibility with various devices and power systems and control technologies that advance decentralization and autonomy. We will implement these cutting-edge technologies and digital transformation (DX) initiatives based on close collaboration between multiple businesses. In October, OMRON established the Power Electronics Center, which oversees the research and development pipeline in the power electronics domain, enhancing development productivity consistently from technology exploration through to product and service development.
In intellectual property and intangible asset initiatives, OMRON is promoting ambidextrous IP activities by combining the “exclusive type” and “sharing & resonating type” approaches (see Figure 5).
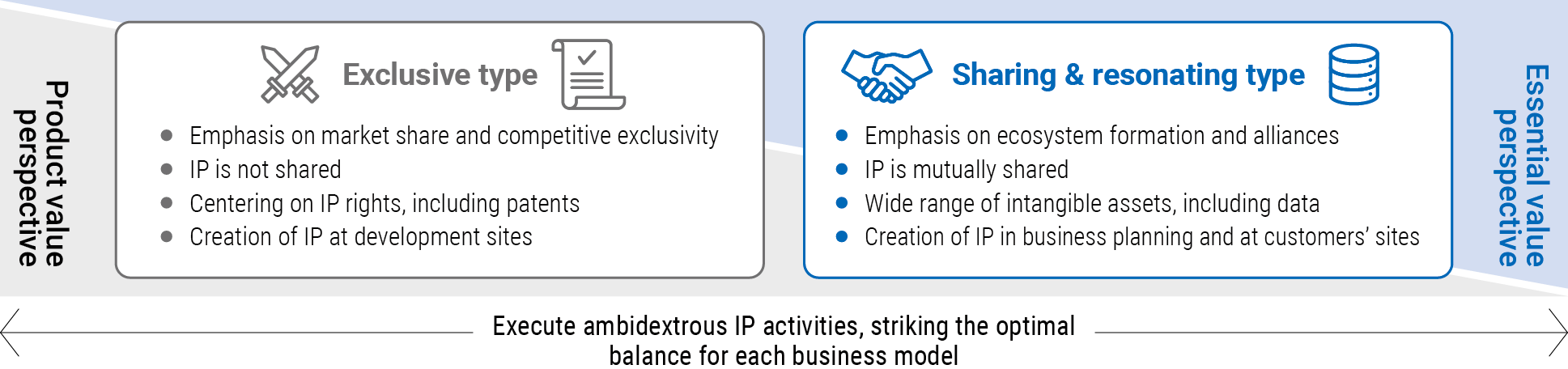
These ambidextrous IP activities combine two approaches: one that secures technologies and know-how as the Company’s competitive advantages, and the other that promotes sharing and standardization in ways that contribute to the development of the entire industry.
In the power electronics domain, OMRON already holds hundreds of patents in addition to extensive know-how, and is visualizing its portfolio of intellectual property and intangible assets from the perspectives of solutions based on both products (hardware) and solutions that combine products and services, while strengthening each in accordance with the characteristics of the respective businesses (see Figure 6).
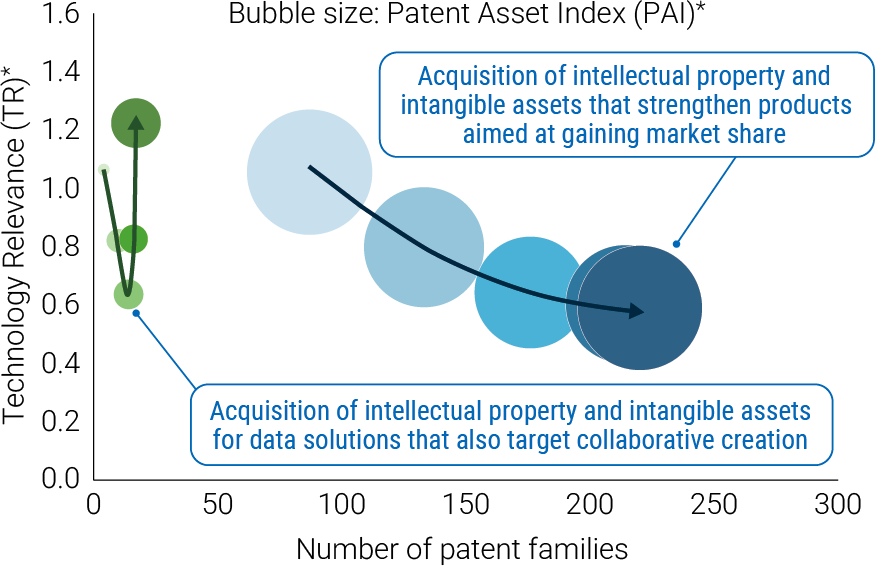
* Transition of OMRON’s patent portfolio over the past five years, created by the Company using LexisNexis® PatentSight+™, a patent analysis tool provided by LexisNexis.
* PAI: Patent Asset Index™ — an indicator representing the competitive advantage and overall value of a patent portfolio
* TR: Technology Relevance ™ — an indicator representing the technological value of a patent family
On the products side, OMRON is promoting the acquisition of intellectual property rights related to the application of technologies that enhance energy efficiency and reliability, focusing on hardware product groups such as general-purpose power supplies and energy storage systems. As for solutions that combine products and services, OMRON’s business units are promoting the acquisition of intellectual property rights in anticipation of future business models in areas aimed at maximizing customer value, by developing solutions such as control algorithms, remote monitoring, and predictive maintenance using data that support these products. By leveraging these intellectual property and intangible assets, we aim to differentiate our products and solutions and clarify business value, while designing the boundary between what to share with external parties and what to keep in-house in the area of data solutions, to drive business expansion including co-creation with partners.
Through these ambidextrous IP activities, we are working to improve the investment efficiency of intellectual property and intangible assets through strategic patent applications that are closely linked to our business models, while contributing to the creation of customer value in the power electronics domain.
Through our technology governance initiatives, we are steadily implementing our technology and intellectual property strategies to identify key focus areas within our core technologies that are closely aligned with our business strategies and to promote their growth. We aim to achieve sustainable growth through the further reinforcement of our core technologies by thoroughly enhancing the competitiveness of our products (hardware) and leveraging these strengths to transform on-site data into solutions through the business that combines products and services.
Topic: OMRON SINIC X’s Initiatives in Exploring Scientific and Academic Value
We are also strengthening initiatives at OMRON SINIC X to explore technologies that contribute to growth from a medium- to long-term perspective. Placing the evolution of machines that contribute to “harmony between humans and machines” in an autonomous society at the core of our R&D activities, we are advancing research under the concept of “evolution of ‘machines’ as AI agents with a physical form and human-like senses.” We actively disseminate our research outcomes to external audiences and promote co-creation through presentations at leading international and domestic conferences as well as participation in exhibitions and other events. Specifically, in fiscal 2024, we submitted approximately 40 research papers to top-tier conferences. We also launched seven new co-creation projects with universities and external research institutions, bringing the total number of co-creation themes, including ongoing ones, to around 20. Not only did we present our research at top-tier conferences, but we also made our first exhibition at TECHNO-FRONTIER 2025 , held at Tokyo Big Sight in July 2025, to demonstrate the value of our research for social implementation and to identify potential co-creation partners. Building on the feedback gained through these exhibitions and presentations, we are deepening concrete dialogues aimed at identifying co-creation partners and advancing social implementation.
